Location 401 Gangseo‐ro, Gangseo‐gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Programme Mixed use, retail
Site Area 1,285 m2
Building Area 719.98 m2
Gross floor Area 5,135.46 m2
Building Scope 10F, 4 basement floors
Parking 78
Height 41.8 m
Building to land ratio 56.03 %
Floor area ratio 399.65 %
Structure Wall Column Structure, RC
Exterior finishing Limestone, Painted aluminum panel
Interior finishing Limestone, granite, artificial stone, eco‐friendly paint
© INTERFACE STUDIOS 2026, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
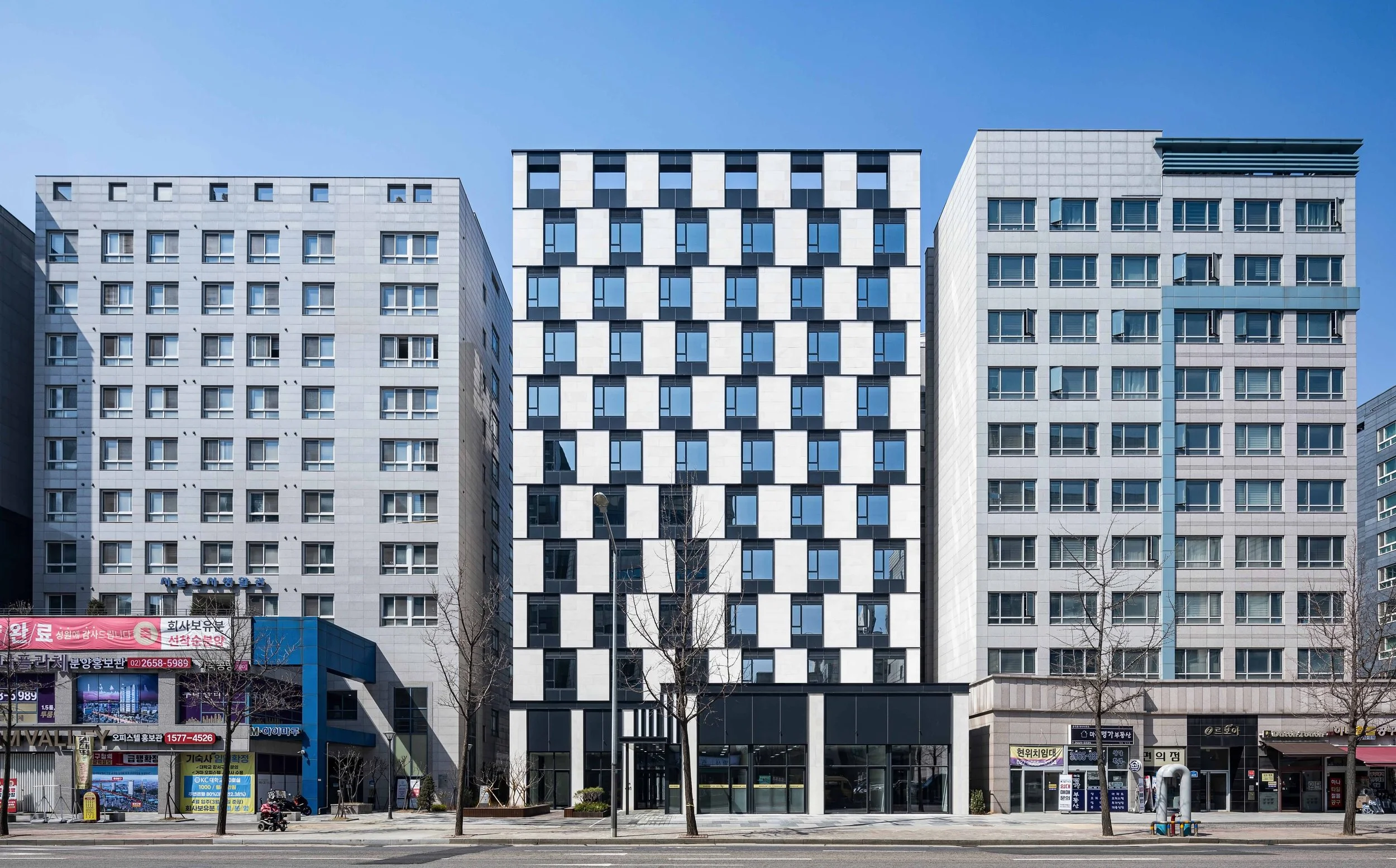
Mixed Use in Magok - Facade
The project site is located along the edge of the Magok Urban Development District Unit Plan and possesses a rare condition for a small-scale site in Seoul: dual frontage and bi-directional accessibility. The eastern frontage faces Gangseo-ro, an eight-lane arterial road, while the rear frontage addresses Magokjungang 8-ro 7-gil, a two-lane internal street. While Gangseo-ro, due to its large scale and the absence of active contextual programs, lacks pedestrian friendliness, Magokjungang 8-ro 7-gil—an internal street within the master plan—reveals strong potential to evolve into a vibrant pedestrian-oriented environment as surrounding office and R&D complexes continue to develop.
Although the project was initially conceived with the objective of maximizing floor area ratio, it simultaneously explores ways in which a private building can incorporate public space and circulation to activate the urban street and provide a meaningful public passage within the block.
Within the rectangular mid-block site—enclosed by neighboring buildings on the north and south and accessed by roads on both sides—the main entrance is positioned to establish a direct relationship with an urban corridor that connects seamlessly to a secondary rear entrance. This corridor is shared by pedestrians, users of the ground-floor neighborhood facilities, and residents, while security for upper-level programs is ensured at the elevator hall. This planar strategy of an internal public corridor offers a space for public movement and social exchange without relying on pilotis or outdoor open spaces. The main entrance is integrated with a publicly accessible open space that functions as both a landscaped area and a resting place for pedestrians. Ground-floor planning prioritizes maximum neighborhood commercial use to encourage active street-level engagement.
The typical floor plan is organized into an optimized and efficient H-shaped layout, achieved through the consolidation of core elements and the 확보 of both front and rear views. Upon arrival at the upper floors via the elevator, occupants encounter a daylight window directly ahead. Adjacent seating areas, combined with corridor glazing that encourages visual intersection, promote casual social interaction among residents of individual units. Pockets generated by the H-shaped configuration are utilized as shared community spaces, including a second-floor terrace and a landscaped rooftop.
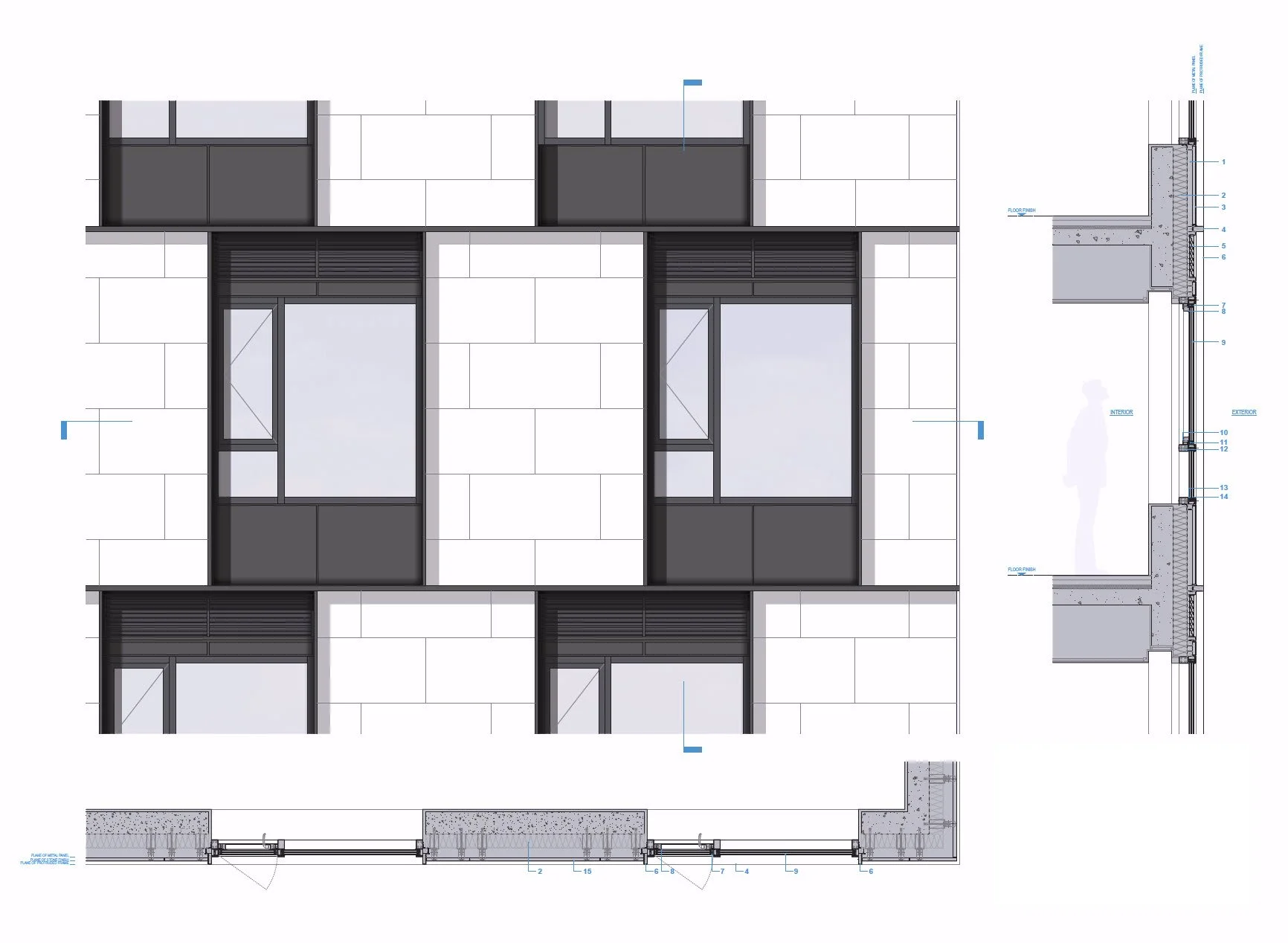
The façade composition responds to alternating bedroom layouts of residential units, resulting in a half-module horizontal shift at each floor and a repeating two-story rhythm. Limestone, the primary façade material, subtly expresses the building’s presence through the natural variation inherent to stone. The façade articulation is carefully developed based on an understanding of light and shadow. Metal panels and glass surfaces are set back 40 mm from the limestone plane, creating depth, while a 30 mm protruded frame extends outward both vertically and horizontally at material junctions and floor lines. This strategy allows each material to exist within its own plane, generating continuous relief across the façade.
This three-dimensional composition, combined with changing daylight conditions, enables multiple visual readings of the building. Furthermore, the alignment of protruded frames produces an optical effect of diagonal misalignment across the elevation, introducing visual dynamism and offering opportunities for interaction between the street, the building, and its occupants within an otherwise monotonous urban context.
마곡 업무 근린 생활시설 — 입면
프로젝트의 대지는 마곡 도시개발사업 지구단위계획의 가장자리에 위치하고 있으며, 동측 전면부에 8차선도로인 강서로를 면하고 후면부에는 2차선 도로 마곡중앙8로7길을 면하는 서울에서 소규모 부지로써 흔치 않은 양방향 접근성을 가지고 있다. 강서로는 가로의 스케일과 주변 컨텍스트 프로그램의 부재로 보행자 친화적인 도로가 아닌 반면, 마스터플랜의 내부 이면도로에 해당하는 마곡중앙8로 7길은 진행중인 주변 업무, 연구 복합시설의 개발과 더불어 매력적인 보행자 도로로의 발전 가능성을 발견할 수 있었다. 프로젝트는 태생적으로 용적률 최대화를 목표로 초점을 맞추며 기획되었지만, 사적 건물에 공적인 공간과 동선 유입에 대해 고민함으로써 도시가로를 활성화시키고 공공적 연결통로를 제공하는 대안을 찾고자 시도하였다.
양방향 접근성의 도로와 남,북이 인접 대지 건물에 둘러싸인 mid-block 형태의 직사각형 땅에서 건물의 주출입구를 배치하고 후면부의 부출입구와 직접적으로 연결되는 Urban corridor를 만들어 보행자, 1층 근린생활시설 이용자, 세대민이 공유하게 하였으며, 엘리베이터 홀에서 상층부의 프로그램에 대한 보안성을 확보하도록 고려하였다. 이러한 공공 복도(urban corrido)의 평면적 시도는 필로티나 outdoor 공간 없이도 사람들에게 공적인 이동과 소통의 통로를 제공한다. 주출입구는 보행자 휴식공간이자 조경공간인 공개공지와 연계하여 배치되었으며, 지상층에 최대의 근린생활시설을 배치하여 가로활동이 활성화될 수 있도록 고려하였다. 기준층의 평면은 코어 요소의 집중배치, 정면/후면 조망의 확보를 통해 최적화된 효율적 ‘H’형 레이아웃으로 구성되었다. 엘리베이터로 상부층에 도착하면 채광창을 정면으로 마주하게 되며, 이와 함께 배치된 seating area는 시선 교차를 장려하는 복도 채광창과 더불어 개별 unit 세대민들의 소통을 제안한다. ‘H’형 레이아웃에서 기인하는 pocket에는 2층 테라스, 옥상 조경공간의 커뮤니티 공유공간을 배치하였다. 입면은 주거 유닛의 침실 레이아웃 방향 뒤집기(반전)에 따라 층마다 반 모듈만큼 쉬프트되어 2층으로 엮인 반복으로 구성된다. 입면의 주재료인 라임스톤은 천연석 특유의 미묘한 텍스쳐 변화(variation)를 통해 은은하게 건물의 존재를 드러낸다. 입면 디자인은 빛과 그림자에 대한 이해를 바탕으로 신중하게 입체화 되었다. 메탈패널/유리 마감의 바깥면은 라임스톤의 바깥면보다 보다 40mm안쪽으로 배치되어 단차를 두었으며, 두 재료의 경계부와 층간 경계에는 수직, 수평방향으로 30mm가 바깥쪽으로 돌출된 protruded frame을 배치함으로써 각각의 재료들은 자기 고유의 평면에 존재하게 되며 지속적인 단차를 만들어낸다. 이는 변화하는 주광 상황과 더불어 다양한 시각적 해석을 가능하게 하기위한 입체적인 구성전략이다. 또한, 돌출면이 정렬된 프레임(Protruded Frame)은 전체 입면에서 사선의 엇갈림의 착시효과를 만들어내며 단조로운 가로에서 길과 건물, 사람 간의 소통의 기회를 제공할 것이다.