외피의 재정의
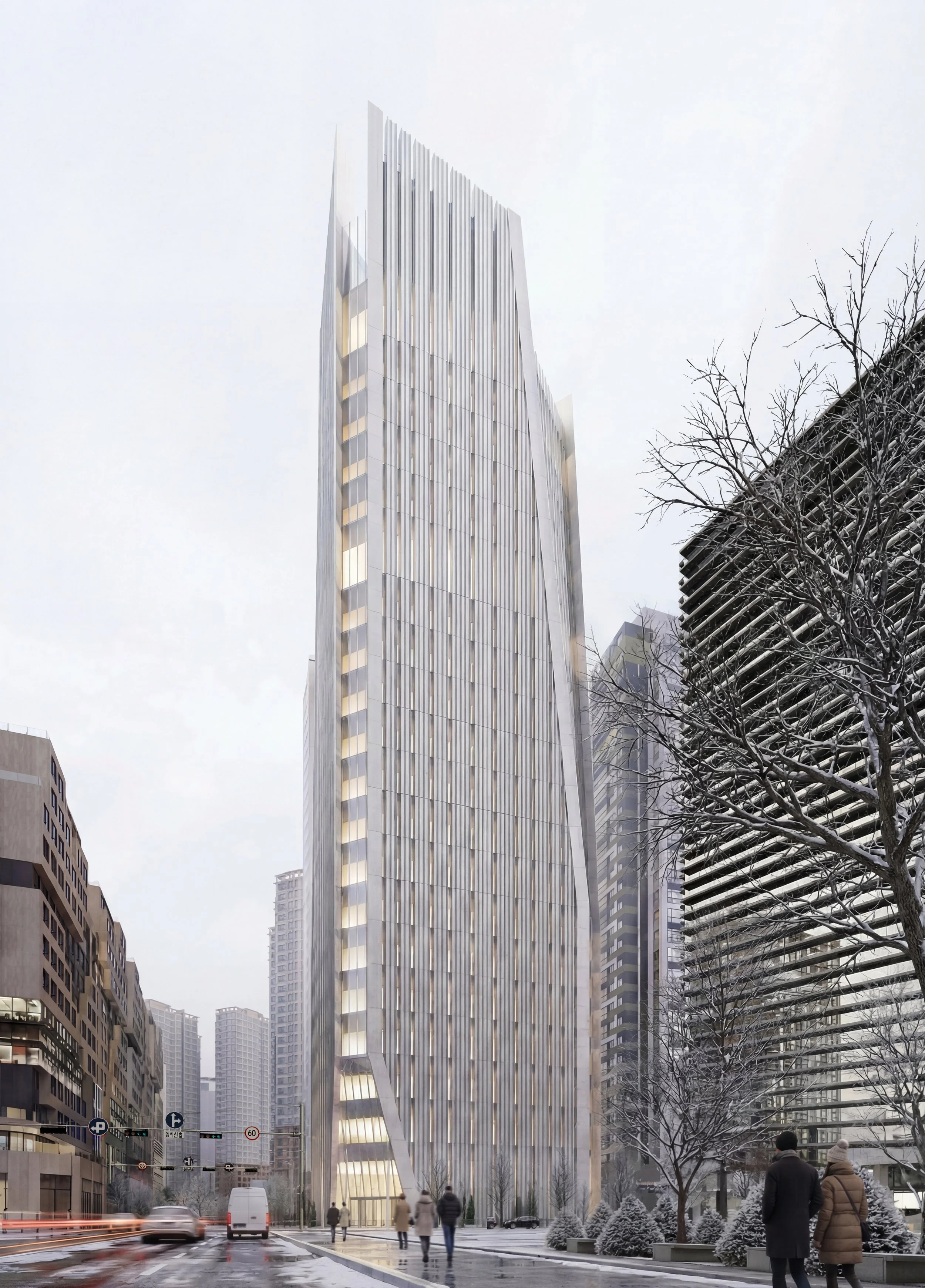
본 제안은 건축의 외피를 단순한 마감재나 차폐막이 아닌, 내·외부 환경을 매개하는 인터페이스로 재정의하는 것에서 시작한다. 건축주의 요구인 딤플(Dimple) 형상의 유지, 공사비 절감, 전면 유리 지양, 그리고 블라인드 없는 공간 구현은 개별적인 조건이 아니라 하나의 통합된 건축 시스템을 통해서 해결된다.
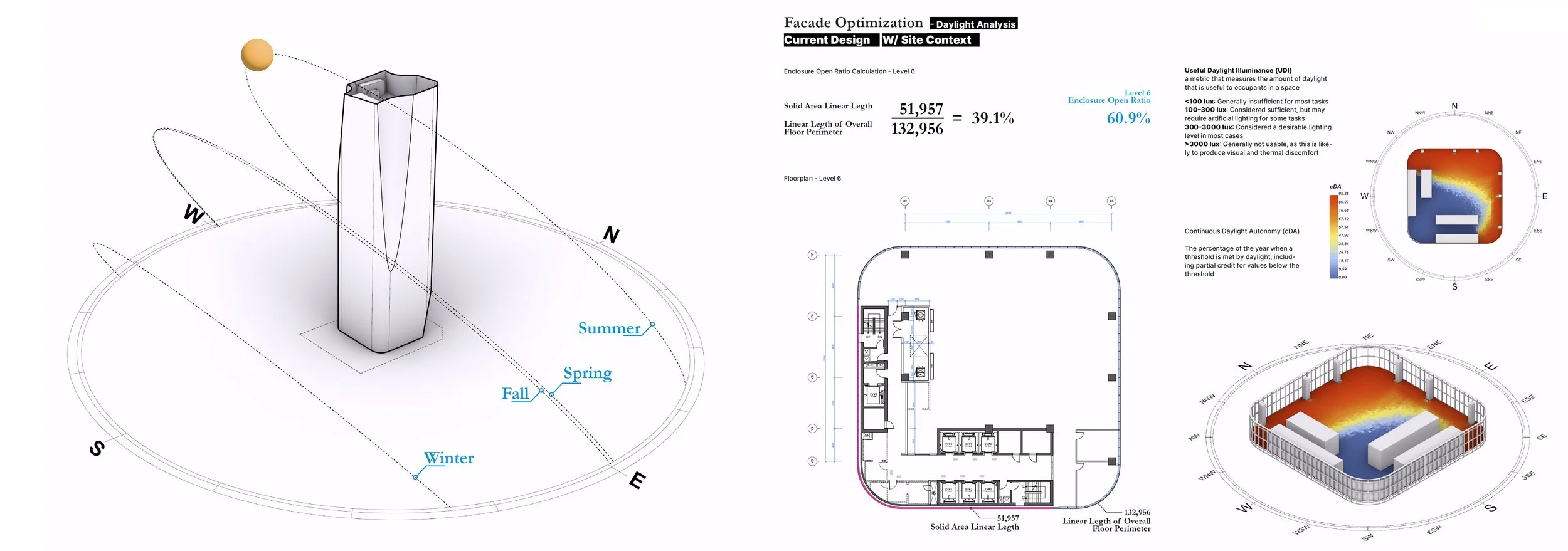
지오메트리 합리화와 구축적 경제성 (Geometric Rationalization)
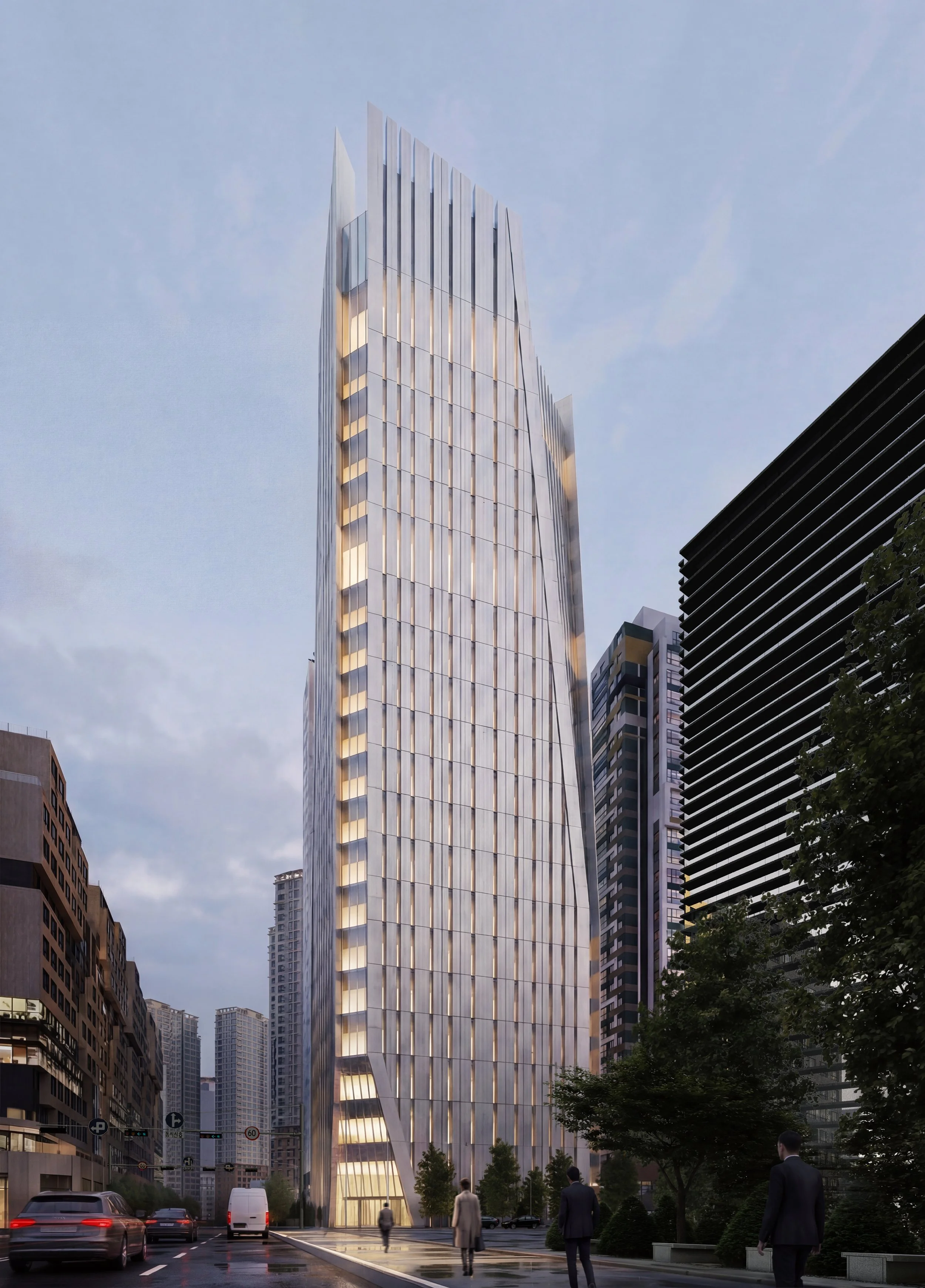
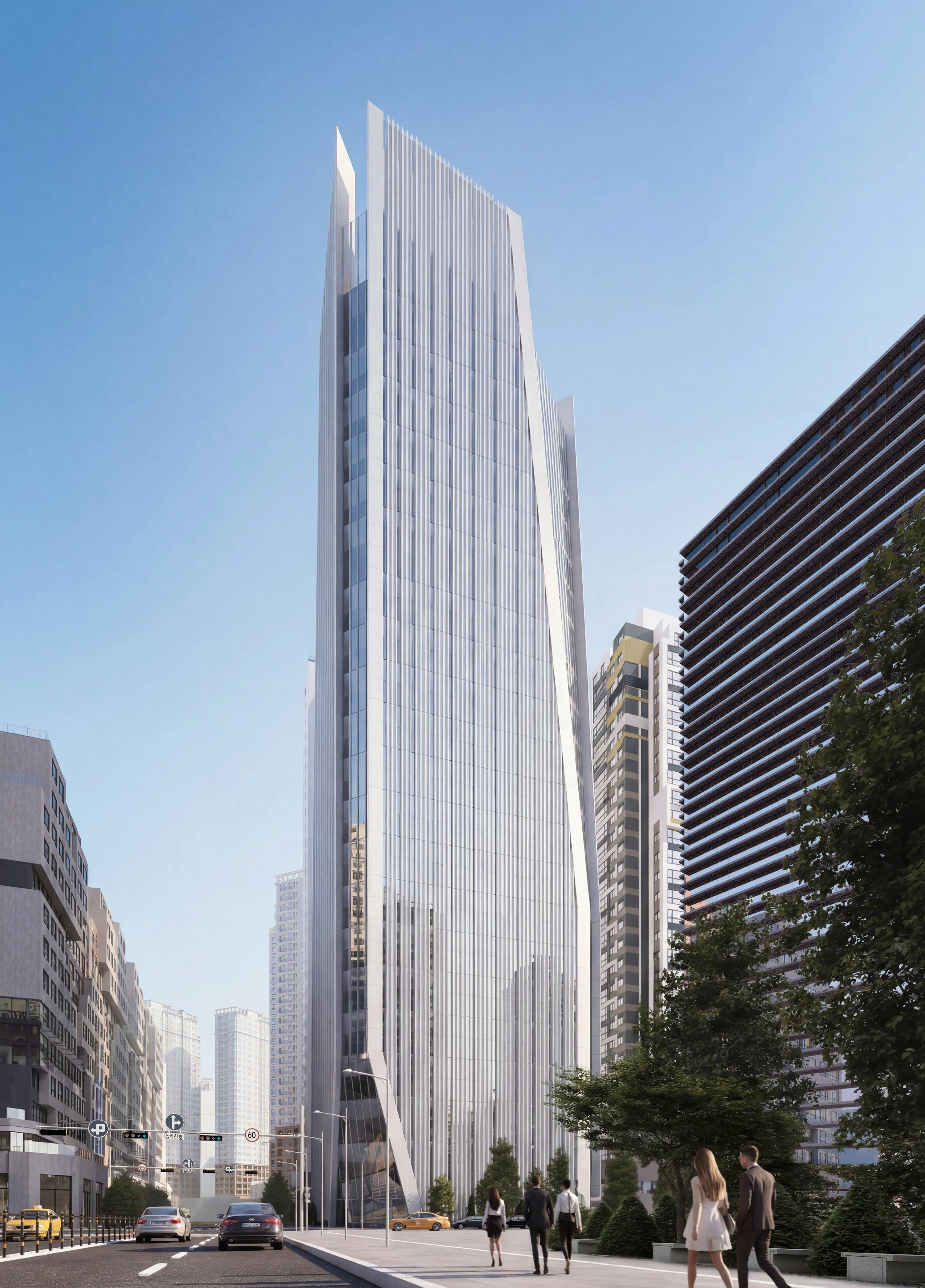
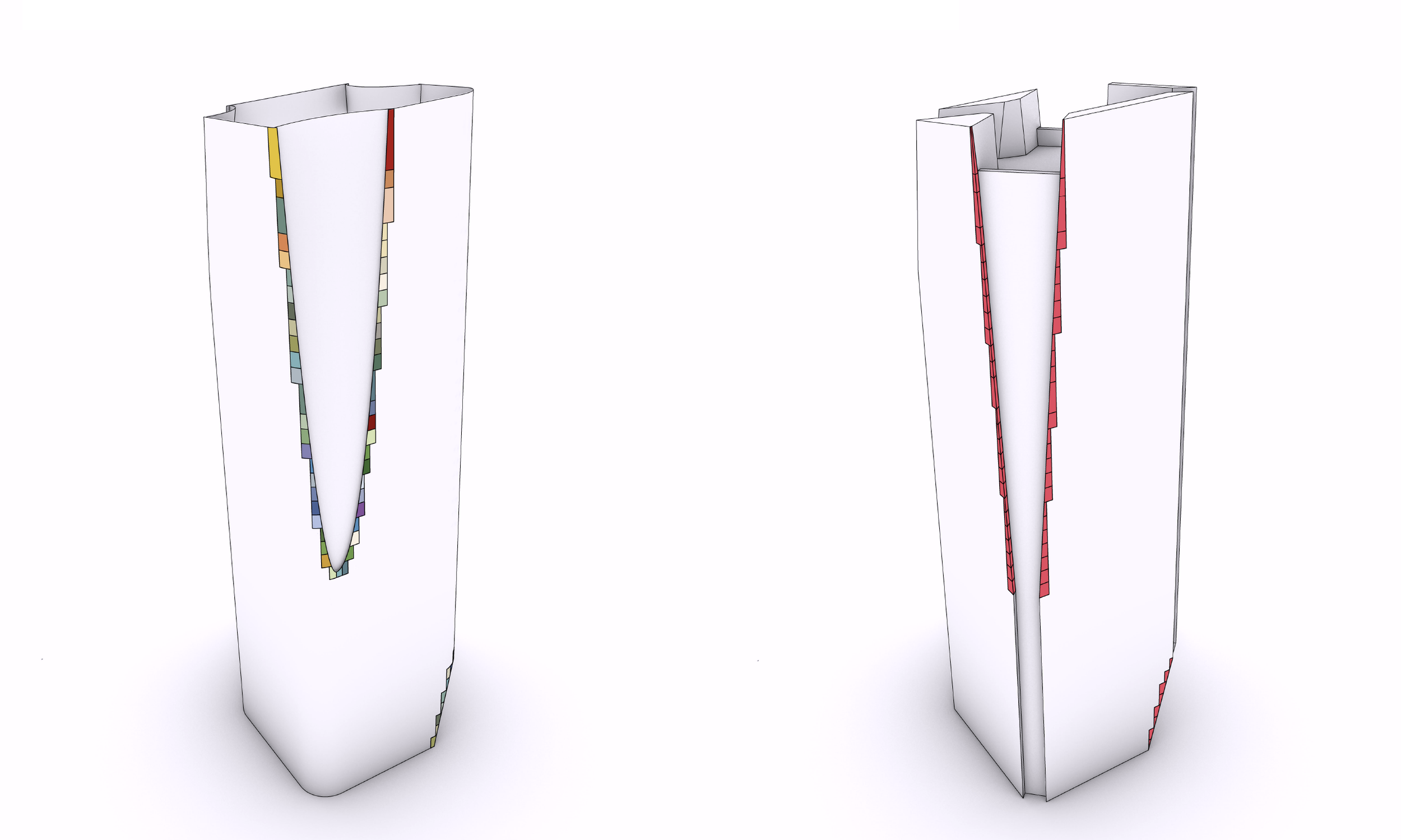
딤플 형상은 단순한 형태가 아니라 타워의 정체성을 결정짓는 핵심 요소이다. 그러나 이중 곡면(Double Curvature) 유리 간의 접합 및 교차는 전 세계적으로도 유례를 찾기 힘든 고난이도의 시공 과제로 시공성과 비용 증가를 만드는 주된 요소이다. 본 설계는 이를 해결하기 위해 타워의 지오메트리를 분석하여 합리화하였다. 곡면 유리구간을 경사진 평판 유리로 대체하되, 사옥 타워의 수직적 연속성과 저층부 입구의 가시성, 상부 특수 프로그램을 드러내는 원안의 아이디어는 존중함으로써, 시각적 깊이감은 유지되고 자재의 효율성은 극대화된다. 이러한 모듈러 시스템은 GFRC 대량 생산을 가능하게하여, 비정형 건축이 가진 복잡한 공정과 과도한 비용 문제를 획기적으로 해결한다.
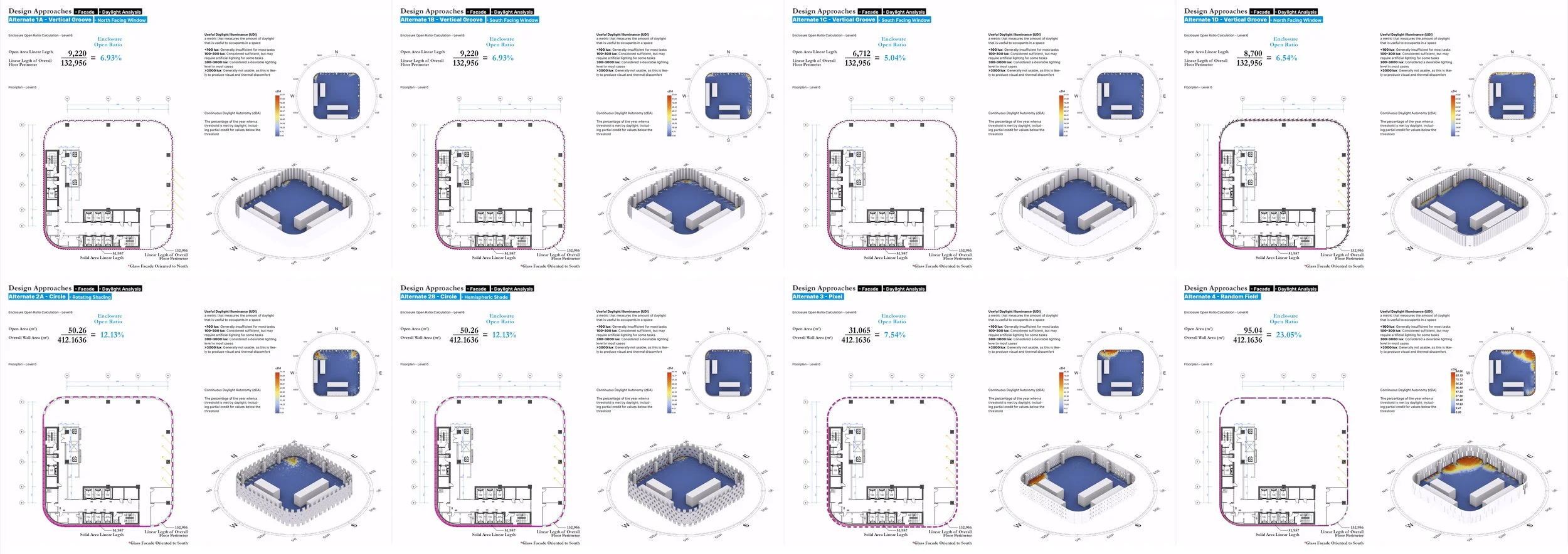
빛의 조율과 제어된 투명성 (Controlled Transparency)
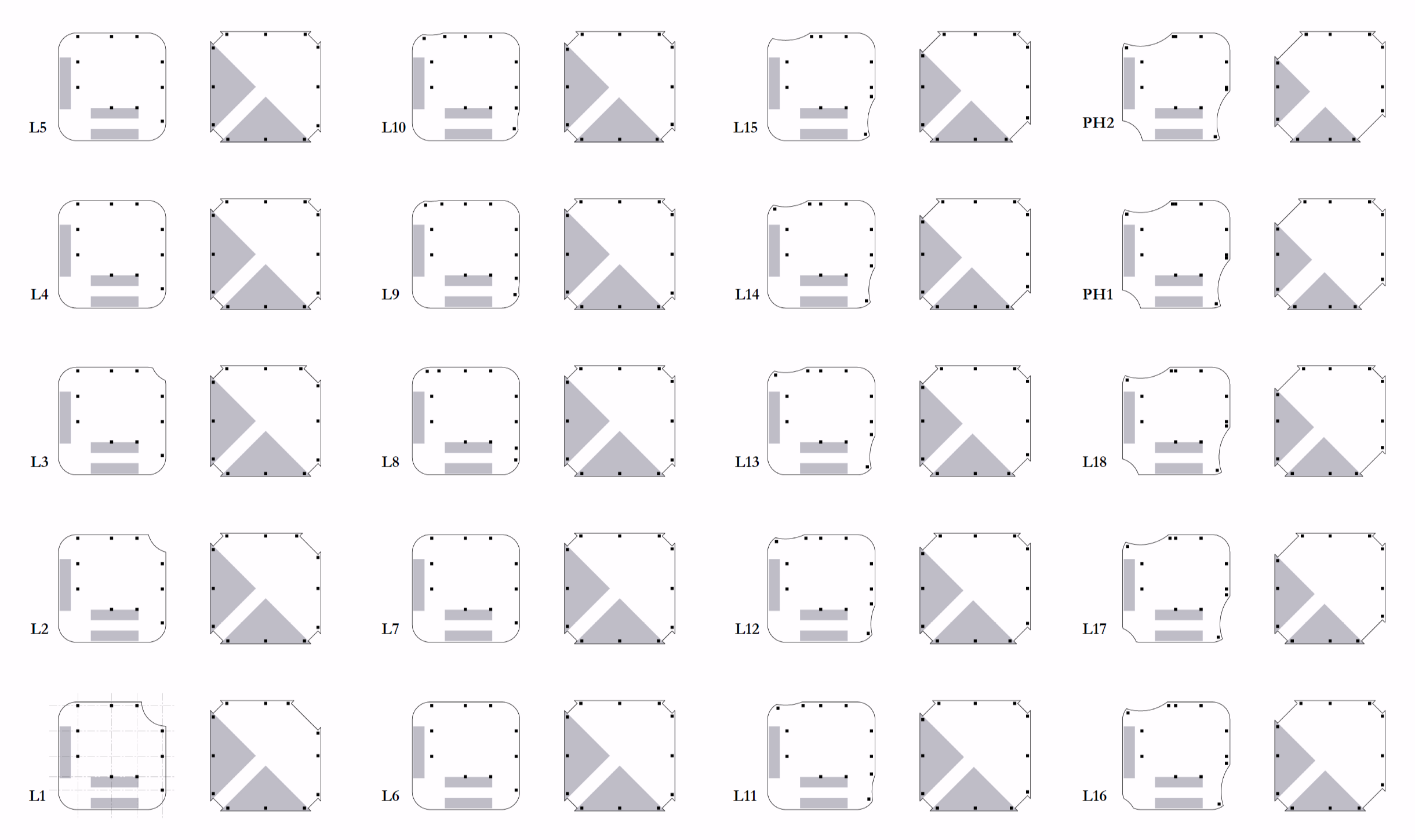
전면 유리 대신 채택된 GFRC외피는 거대한 ‘광학적 필터’로 작동한다. 향(Orientation)에 기반하여 리드미컬하게 배치된 입면 요소와 최적화된 창면적비는 강한 직사광을 부드러운 간접광으로 전환하며 내부공간으로 유입되는 자연관을 부드럽게 확산시킨다. 또한 깊게 패인 개구부는 채광과 조망을 확보함과 동시에 프라이버시와 단열 성능을 보장한다. 즉, 투명성은 무조건적인 개방이 아닌 정교하게 조절된 상태로 제공된다.
일체화된 차양 시스템 (Integrated Shading)
별도의 블라인드는 더 이상 필요하지 않다. 차광 기능은 부가적인 요소에 의존하는 것이 아니라, 건축의 형상 그 자체에 내재화(Internalized)되어 마치 고도로 디자인된 고대의 기계장치처럼 작동한다. 이는 유지관리 수요를 최소화할 뿐만 아니라, 태양의 이동에 따라 시시각각 표정이 변하는 입체적인 입면을 완성하고, 주야 시간에 다르게 표출되는 정체성을 확보한다.
본 프로젝트의 외피는 내·외부를 가르는 수동적 경계가 아니라, 환경 성능을 수행하고 타워의 정체성을 구축하는 핵심적인 건축적 장치이다. 경제성, 기능성, 심미성이 입면 안에서 결합되고 통합되며, 건축주의 요구사항은 이 프로젝트의 디자인 논리를 확립하는 가장 강력한 동력이 될 수 있었다.
© INTERFACE STUDIOS 2026, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
마이다스아이티 정자동 신사옥
Redefining the Building Envelope
This proposal begins by redefining the architectural envelope not as a mere finishing layer or protective barrier, but as a responsive interface that actively mediates between interior and exterior environments. The client’s requirements—maintaining the dimple geometry, reducing construction costs, avoiding a fully glazed façade, and achieving spaces without blinds—are not treated as isolated constraints. Instead, they are resolved through a single, integrated architectural system.
Geometric Rationalization and Constructive Economy
The dimpled form is not a decorative gesture but a defining element of the tower’s identity. However, the junctions and intersections of double-curved glass represent an exceptionally complex construction challenge, rarely realized even on a global scale, and are a primary driver of excessive cost and constructability risk. To address this, the design rigorously analyzes and rationalizes the tower’s geometry. Curved glass surfaces are replaced with inclined planar glazing, while preserving the original intent: the vertical continuity of the office tower, the visual legibility of the lower-level entrance, and the expression of specialized programs at the upper levels. Through this approach, visual depth is retained while material efficiency is significantly enhanced. The resulting modular system enables the mass production of GFRC panels, fundamentally resolving the procedural complexity and cost escalation typically associated with free-form architecture.
Light Modulation and Controlled Transparency
In place of a fully glazed façade, the GFRC envelope operates as a large-scale optical filter. Facade elements, rhythmically arranged according to orientation, and an optimized window-to-wall ratio transform harsh direct sunlight into soft, diffuse illumination, gently distributing natural light into the interior. Deeply recessed openings secure daylight and views while simultaneously ensuring privacy and thermal performance. Transparency, therefore, is not conceived as indiscriminate openness, but as a precisely calibrated condition.
Integrated Shading System
Separate blinds are no longer necessary. Shading is not an applied accessory but is internalized within the architectural form itself, operating like a finely tuned, ancient mechanical device embedded in the building’s geometry. This approach minimizes maintenance demands while generating a richly articulated façade whose expression continuously shifts with the movement of the sun. The building acquires a differentiated identity across day and night, time and season.
In this project, the envelope is not a passive boundary dividing inside from outside, but a critical architectural apparatus that performs environmental functions while constructing the tower’s identity. Economy, performance, and aesthetics are synthesized within the façade, and the client’s requirements become the most powerful catalyst in establishing the project’s design logic.
MidasIT Headquarters Tower
Location 63, Jeongja-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea
Programme Office, Educational Research Facilities, Cultural and Assembly Facilities
Site Area 2,832.2 m2
Building Area 1,465.71 m2
Gross floor Area 33,586.89 m2
Building Scope 20F, 7 basement floors
Parking 223
Height 119.87 m
Building to land ratio 51.75 %
Floor area ratio 673.85 %
Structure Composite - Steel Frame, RC
Exterior finishing GFRC, Painted aluminum panel
Interior finishing Limestone, granite, artificial stone, eco‐friendly paint
© INTERFACE STUDIOS 2026, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED